The Technology Blog

How AI is Helping Detect Diseases Earlier
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing healthcare by improving disease diagnosis. AI helps doctors find conditions like cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders earlier. By using machine learning healthcare tools, AI can analyse large amounts of medical data, spot patterns, and assist healthcare workers in making quick, precise diagnoses.
Early detection is vital for better patient outcomes. It allows for timely interventions and effective treatment plans. With advancements in AI for early detection, healthcare systems in the UK and worldwide are becoming more efficient. This reduces misdiagnoses and boosts survival rates for serious illnesses.
This article discusses how AI is transforming disease detection, its benefits, and the challenges of integrating AI into healthcare.
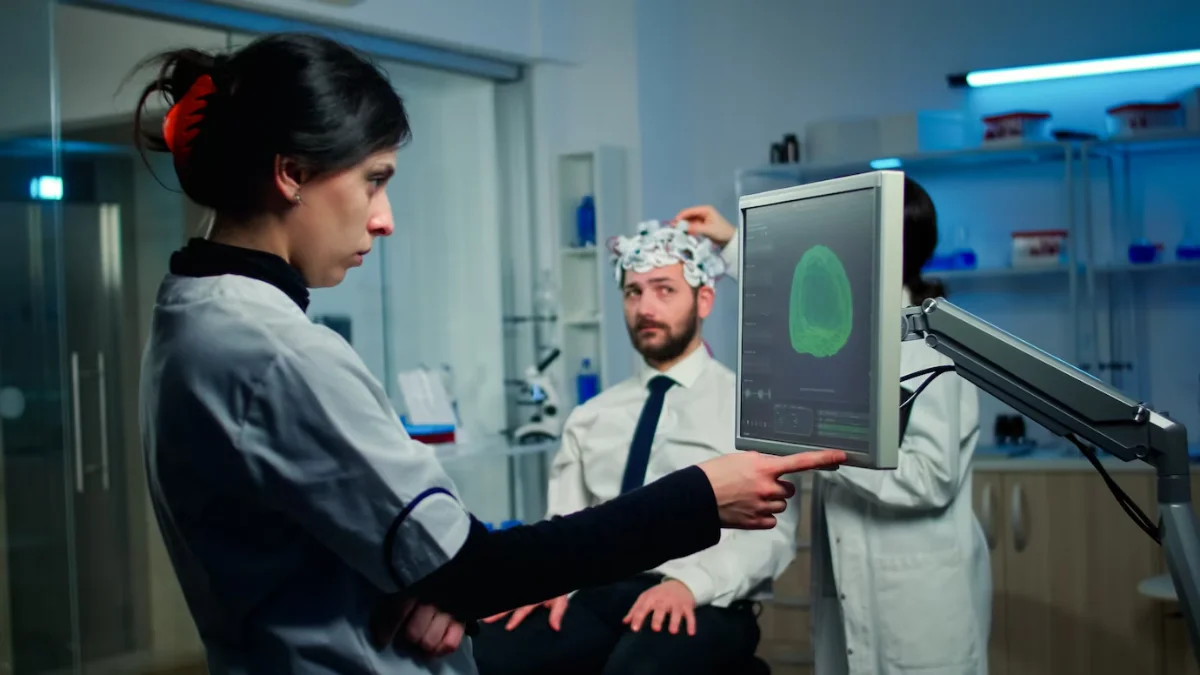
The Role of AI in Medical Diagnosis
How AI Works in Disease Detection
AI uses machine learning algorithms to process big datasets like medical records and imaging scans. These algorithms learn to identify patterns linked to specific diseases and find abnormalities that human doctors might overlook.
Key AI technologies in medical diagnosis include:
- Deep Learning – Neural networks that mimic brain function, enabling AI to learn from extensive medical datasets.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – AI analyses medical texts and patient histories to aid diagnosis.
- Computer Vision – AI interprets medical images like X-rays and MRIs, detecting early disease signs.
- Predictive Analytics – AI uses past patient data to predict disease risks, allowing for preventive care.
- AI Chatbots and Virtual Assistants – These tools help with initial assessments by analysing patient symptoms and suggesting possible conditions.
By using these technologies, healthcare providers can boost diagnostic accuracy, lower human error, and speed up decision-making.
The Benefits of AI in Medical Diagnosis
Integrating AI in medical diagnosis brings many advantages, including:
- Faster Diagnosis – AI analyses scan and test results in minutes, reducing patient wait times.
- Higher Accuracy – Machine learning can spot subtle patterns that human eyes may miss, increasing diagnostic precision.
- Reduced Workload for Doctors – AI automates routine tasks, letting doctors focus more on patient care.
- Early Disease Detection – AI can find potential health issues before symptoms appear, allowing for earlier interventions.
- Personalised Medicine – AI tailors treatment plans based on individual patient data, enhancing treatment effectiveness.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare – AI cuts the need for expensive tests by providing quicker, more efficient assessments.

Machine Learning Healthcare Applications in Early Disease Detection
1. AI in Cancer Detection
Cancer is a leading cause of death, but early detection can improve survival rates. AI is vital in spotting various cancers, including:
- Breast Cancer – AI-powered mammograms can find tumours earlier than traditional methods.
- Lung Cancer – AI-enhanced CT scans can detect small nodules indicating early-stage lung cancer.
- Skin Cancer – AI analyses mole images to assess melanoma risk, reducing unnecessary biopsies.
- Colorectal Cancer – AI-assisted colonoscopy tools effectively find polyps and early signs of colorectal cancer.
AI’s ability to quickly process imaging data allows oncologists to diagnose and treat cancer earlier, improving outcomes.
2. AI in Neurological Disorders
AI for early detection of neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s is changing neurology. AI can:
- Analyse speech patterns and cognitive tests for early dementia signs.
- Monitor motor functions to identify irregularities signalling Parkinson’s disease.
- Predict disease progression, aiding in personalised treatment strategies.
- Spot changes in brain images that suggest early-stage neurodegenerative diseases.
Early intervention can slow disease progression and enhance patients’ quality of life.
3. AI in Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis
Heart disease is a major health issue in the UK. AI helps detect cardiovascular conditions by:
- Analysing electrocardiograms (ECGs) for irregular rhythms and arrhythmias.
- Predicting heart attack risks using patient health data.
- Identifying early hypertension signs and recommending lifestyle changes.
- Assessing arterial plaque build-up and offering stroke prevention insights.
AI tools enable doctors to deliver targeted treatments and reduce heart disease risks.
4. AI in Diabetes Prediction and Management
Diabetes is a rising health challenge, but AI is crucial in predicting and managing it. AI applications include:
- Identifying individuals at high risk for type 2 diabetes based on lifestyle factors.
- Analysing continuous glucose monitoring data for personalised insulin recommendations.
- Predicting complications like retinopathy by examining retinal scans.
- Providing AI-driven lifestyle advice to prevent diabetes onset.
AI helps healthcare providers reduce complications related to diabetes and enhance outcomes.
5. AI in Infectious Disease Surveillance
AI is essential in tracking and predicting infectious diseases like COVID-19. AI models can:
- Analyse real-time data to forecast outbreaks and trends.
- Identify high-risk individuals and groups.
- Assist in vaccine development by studying virus mutations.
- Monitor treatment efficacy through patient response assessments.
Using machine learning healthcare solutions, public health officials can respond more effectively to outbreaks.

Challenges and Ethical Considerations of AI in Healthcare
1. Data Privacy and Security
AI needs a lot of patient data, raising privacy and security concerns. To ensure ethical use, AI in healthcare must follow regulations like the UK’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
2. Bias in AI Algorithms
AI models may reflect biases in their training data. If datasets lack diversity, AI might not work equally well for all demographic groups. Ensuring fairness in AI diagnostics is crucial.
3. Integration with Existing Healthcare Systems
AI tools must blend smoothly with current healthcare systems. Many hospitals still use traditional methods, making AI adoption a gradual process that requires training and support for professionals.
4. Ethical Use of AI in Diagnosis
While AI boosts accuracy, final medical decisions should always involve human judgment. Doctors must interpret AI insights responsibly and ensure they align with clinical judgment.
The Future of AI in Early Disease Detection
The future of AI for early detection is bright, with innovations ahead:
- AI-Powered Wearables – Smartwatches will provide real-time data for disease predictions.
- Advanced AI Imaging Techniques – AI-driven radiology will further improve imaging diagnosis.
- AI-Driven Drug Discovery – Machine learning will speed up new treatment development for diseases like cancer.
- AI-Assisted Robotic Surgery – AI-powered robots will enhance surgical precision.
- Telemedicine and AI Diagnosis – AI-driven virtual consultations will enable accurate remote diagnoses.
As AI evolves, it will play a key role in diagnosing diseases sooner, leading to better healthcare for patients in the UK and beyond.